One year into the Digital New Deal initiative, Korea has successfully established sound digital infrastructure and innovative foundations for businesses.
SEOUL, South Korea, Aug. 3, 2021 /PRNewswire/ -- The Born2Global Centre released an article that highlights the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT)'s Korean Digital New Deal. As part of the Korean government MSIT, Born2Global Centre has played a crucial role by connecting Korean startups with various opportunities worldwide.
Digital New Deal Innovates Economy
Since July of last year, the Korean government has implemented the Korean Digital New Deal, a national-level initiative aimed to lift the nation out of a pandemic-battered economy.
Exactly one year into its implementation, the initiative has led the Korean economy beyond the pandemic crisis, promoting innovation across all industries.
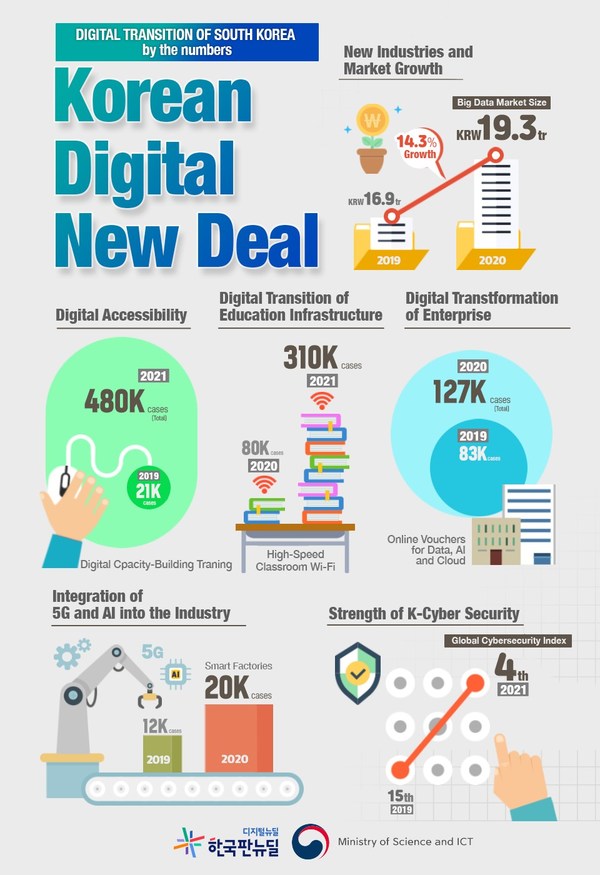
Over the last year, the MSIT, along with other government departments, has put an enormous budget amounting to KRW 10.1 trillion (USD 8.7 billion) into the development of leading digital technologies, including big data, artificial intelligence (AI) and the 5th generation (5G) mobile network.
As a result, the pan-government initiative has produced good results, particularly in building integrated data platforms for public use. "Data Dam," one of the core projects, helped to promote the utilization of useful data across the private sector, such as big data and AI-based learning data. More than 4,300 types of data related to finance, transportation, culture, and healthcare were collected and put to public use through the newly established data platforms. According to the ministry, the domestic data market has grown by 14.3 percent compared to the previous year.
The government has also supported businesses, especially smaller-sized ones, in digitalizing their facilities, like plants and stores. The effort aimed to help the businesses adapt to the rapidly transforming landscape of industries with growing demand for non-face-to-face transactions and online services. The digitalized facilities resulted in improving their productivity by 28 percent.
In addition, around 127,000 small and medium-sized companies were allowed to access and purchase public data at a discounted price through the government voucher system.
The Digital New Deal policy is also lauded for its contribution to mitigating the post-pandemic unemployment crisis by involving small businesses and human resources in many projects. In fact, more than 170,000 organizations and companies have so far engaged in the Digital New Deal's projects, 95 percent of which are small and medium-sized companies as well as startups. More than 90,000 workers, including youth interns, were part of the projects as well.
Efforts have been made to identify and improve regulations and the existing legal system that could hinder the efficient and innovative functioning of digital markets. The improved system also brought about active investment across the private sector, for example, with large-scale contracts worth KRW 110 billion (USD 95 million) signed in the cloud sector.
Inclusive Digital Economy
One of the core objectives of the Korean Digital New Deal is to provide "people-centric" digital services and infrastructure that allow every individual to benefit from digital technologies.
Over a year of pursuing the initiative, a variety of digital services have been developed and distributed for public use from education and healthcare to culture and welfare.
For instance, "Dr. Answer," an AI-based precision diagnostic solution, has kept people healthy by providing tailored disease prediction, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. An intelligent early warning system for natural disasters such as floods has been set up across the country to secure people's safety.
To build a digital infrastructure inclusive to all individuals, high-powered wireless Internet was installed in more than 310,000 classrooms of elementary, middle, and high schools across the country. Around 1,000 "Digital Learning Centers" provide educational programs on digital technology for the underprivileged. In addition, more than 10,000 high-speed Internet systems were set up at public spaces, like bus stops, as well as across rural areas, to help narrow the gap of digital access among the people.
The impact of the ongoing Digital New Deal programs was reflected positively in international indexes of digital technology. The ministry said that in 2020 Korea placed eighth among 63 countries, up from 10th in 2019, in digital competitiveness measured by the International Institute for Management Development (IMD). The nation came in seventh on Oxford Insights' "Government AI Readiness Index 2020," jumping 19 spots from 2019. The indicator measures the extent of governments' willingness to use AI technologies.
In the meantime, the ministry recently released an updated version of the initiative, dubbed "Digital New Deal 2.0." Under the revised policy, the ministry is speeding up the implementation of the key projects as well as newly added programs, with the aim of extending the benefits of the initiative to broader society.
For more detailed information on Korean Digital New Deal, visit https://digital.go.kr/front/main/eng.do.
Media contact: